 Ebb and flow is one of the most preferred ways of doing Hydroponics gardening. This system is active as well as recovery type. Also known as flood and drain this system is quite easy to understand. The plant is kept in a reservoir containing nutrient solution. When the pump is started the nutrient are pumped in to the plant. After the water reaches the determined level, it is drained in to a river while the oxygen is sucked by the roots.
Ebb and flow is one of the most preferred ways of doing Hydroponics gardening. This system is active as well as recovery type. Also known as flood and drain this system is quite easy to understand. The plant is kept in a reservoir containing nutrient solution. When the pump is started the nutrient are pumped in to the plant. After the water reaches the determined level, it is drained in to a river while the oxygen is sucked by the roots.2. Nutrient film technique
 Nutrient technique is also a recovery type active Hydroponic system. In this kind of hydroponics system a submersible pump is used and the roots are suspended in a grow tube. The grow tube is in such an angle that the solution of the nutrients get recycled by flowing over the roots and then coming back to the reservoir. The oxygen requirement is solved by making use of air stones or air stones. This system is highly effective and a bit difficult to build. A single mistake can cause the whole plant to dry.
Nutrient technique is also a recovery type active Hydroponic system. In this kind of hydroponics system a submersible pump is used and the roots are suspended in a grow tube. The grow tube is in such an angle that the solution of the nutrients get recycled by flowing over the roots and then coming back to the reservoir. The oxygen requirement is solved by making use of air stones or air stones. This system is highly effective and a bit difficult to build. A single mistake can cause the whole plant to dry. This is the simplest of all active hydroponics systems. The platform that holds the plants is usually made of Styrofoam and floats directly on the nutrient solution. An air pump supplies air to the air stone that bubbles the nutrient solution and supplies oxygen to the roots of the plants. It can also called Water culture, it is the system of choice for growing leaf lettuce, which are fast growing water loving plants, making them an ideal choice for this type of hydroponics system. Very few plants other than lettuce will do well in this type of system. This type of hydroponics system is great for the classroom and is popular with teachers.
This is the simplest of all active hydroponics systems. The platform that holds the plants is usually made of Styrofoam and floats directly on the nutrient solution. An air pump supplies air to the air stone that bubbles the nutrient solution and supplies oxygen to the roots of the plants. It can also called Water culture, it is the system of choice for growing leaf lettuce, which are fast growing water loving plants, making them an ideal choice for this type of hydroponics system. Very few plants other than lettuce will do well in this type of system. This type of hydroponics system is great for the classroom and is popular with teachers. This method isprobably the most widely used type of hydroponic system in the world. Operation is simple, a timer controls a submersed pump. The timer turns the pump on and nutrient solution is dripped onto the base of each plant by a small drip line.
This method isprobably the most widely used type of hydroponic system in the world. Operation is simple, a timer controls a submersed pump. The timer turns the pump on and nutrient solution is dripped onto the base of each plant by a small drip line. This method is probably the most high-tech type of hydroponics gardening. Like the N.F.T. system the growing medium is primarily air. The roots hang in the air and are misted with nutrient solution.
This method is probably the most high-tech type of hydroponics gardening. Like the N.F.T. system the growing medium is primarily air. The roots hang in the air and are misted with nutrient solution. 

















 in Command Manager, click Circle
in Command Manager, click Circle  . As you can see on upper right corner sketch icon appear indicate that you’re on sketch mode
. As you can see on upper right corner sketch icon appear indicate that you’re on sketch mode .
. no need to be exact the size will define in later step. Press keyboard ESC to end circle sketch.
no need to be exact the size will define in later step. Press keyboard ESC to end circle sketch. , and start dimensioning pick circle edge and set to 0.50in
, and start dimensioning pick circle edge and set to 0.50in 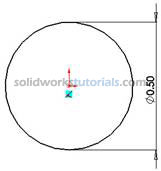 . Press keyboard ESC to end smart dimension.
. Press keyboard ESC to end smart dimension.
 .
.
 , click Normal To
, click Normal To  .
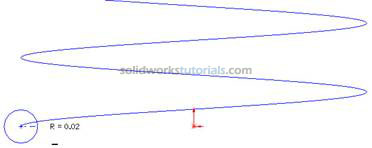
.
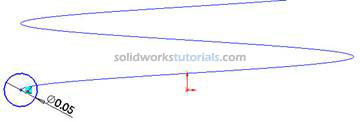
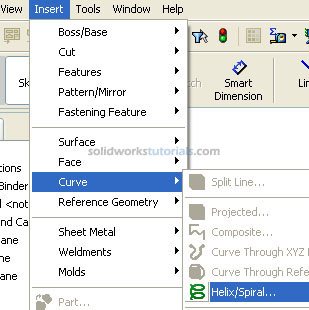
 . Click Features
. Click Features and activate features menu. Click Swept Boss/Base
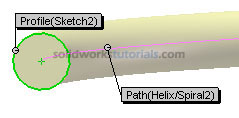
and activate features menu. Click Swept Boss/Base and set Profile to Sketch2 by click on circle sketch
and set Profile to Sketch2 by click on circle sketch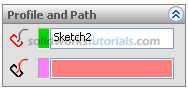
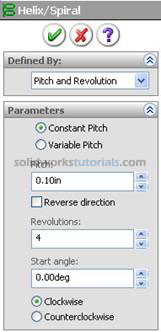
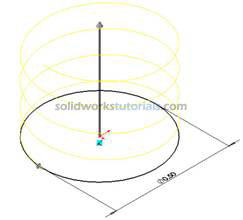
 and set Path by click helix path
and set Path by click helix path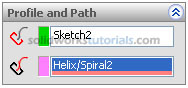
 and
and 
 . As you can see on upper right corner sketch icon appear indicate that you’re on sketch mode
. As you can see on upper right corner sketch icon appear indicate that you’re on sketch mode .
. no need to be exact the size will define in later step. Press keyboard ESC to end rectangle sketch.
no need to be exact the size will define in later step. Press keyboard ESC to end rectangle sketch.
 , and start dimensioning pick vertical line and set to 2.00in , pick horizontal line and set to 2.00in
, and start dimensioning pick vertical line and set to 2.00in , pick horizontal line and set to 2.00in  . Press keyboard ESC to end smart dimension
. Press keyboard ESC to end smart dimension and activate features menu. Click Extruded Boss/Base
and activate features menu. Click Extruded Boss/Base and set D1 to 0.5in
and set D1 to 0.5in and
and 
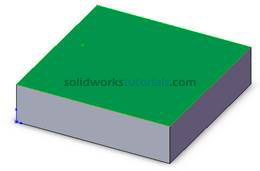 , click Normal To
, click Normal To  . Activate sketch menu by click Sketch
. Activate sketch menu by click Sketch and select Circle
and select Circle . Sketch 4 circle at four edges.
. Sketch 4 circle at four edges. 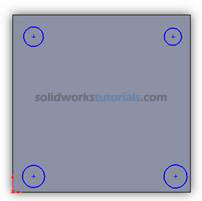
 , set diameter circle to 0.2in . Select distance for edge set to 0.3in
, set diameter circle to 0.2in . Select distance for edge set to 0.3in 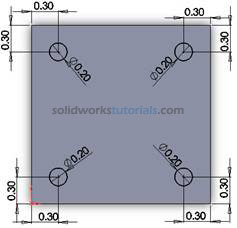 .
. and sketch one circle at center
and sketch one circle at center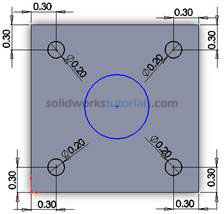 .
. , set diameter circle to 1.0in . Select distance for edge set to 1.0in.
, set diameter circle to 1.0in . Select distance for edge set to 1.0in. 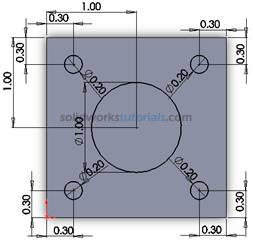
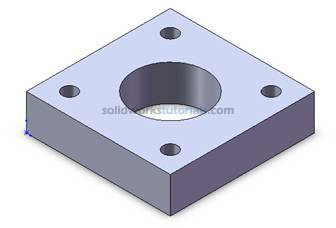
 , click Extruded Cut
, click Extruded Cut , under Direction 1, Through All
, under Direction 1, Through All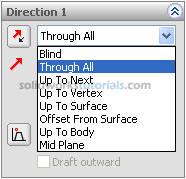 and
and